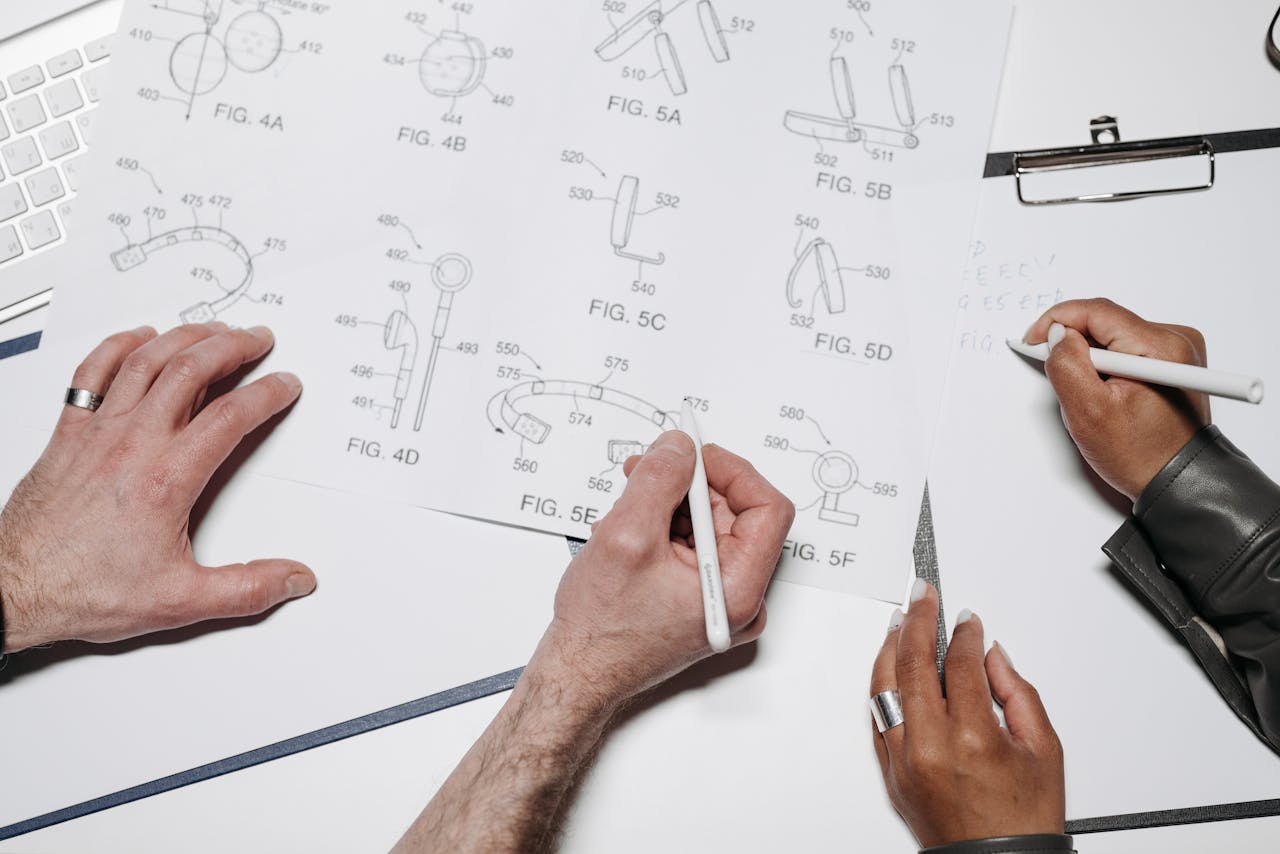
In the realm of intellectual property, the significance of a well-prepared patent drawing cannot be overstated. Utility patents protect new inventions, and accompanying these inventions with precise and detailed drawings is essential for securing patent approval. Engaging in quality patent drawing services can make a key difference in the strength of a patent application and the success of an invention in the marketplace. This article explores the critical elements of utility patent drawings and why they matter for inventors and patent professionals alike.
Understanding Utility Patent Drawings
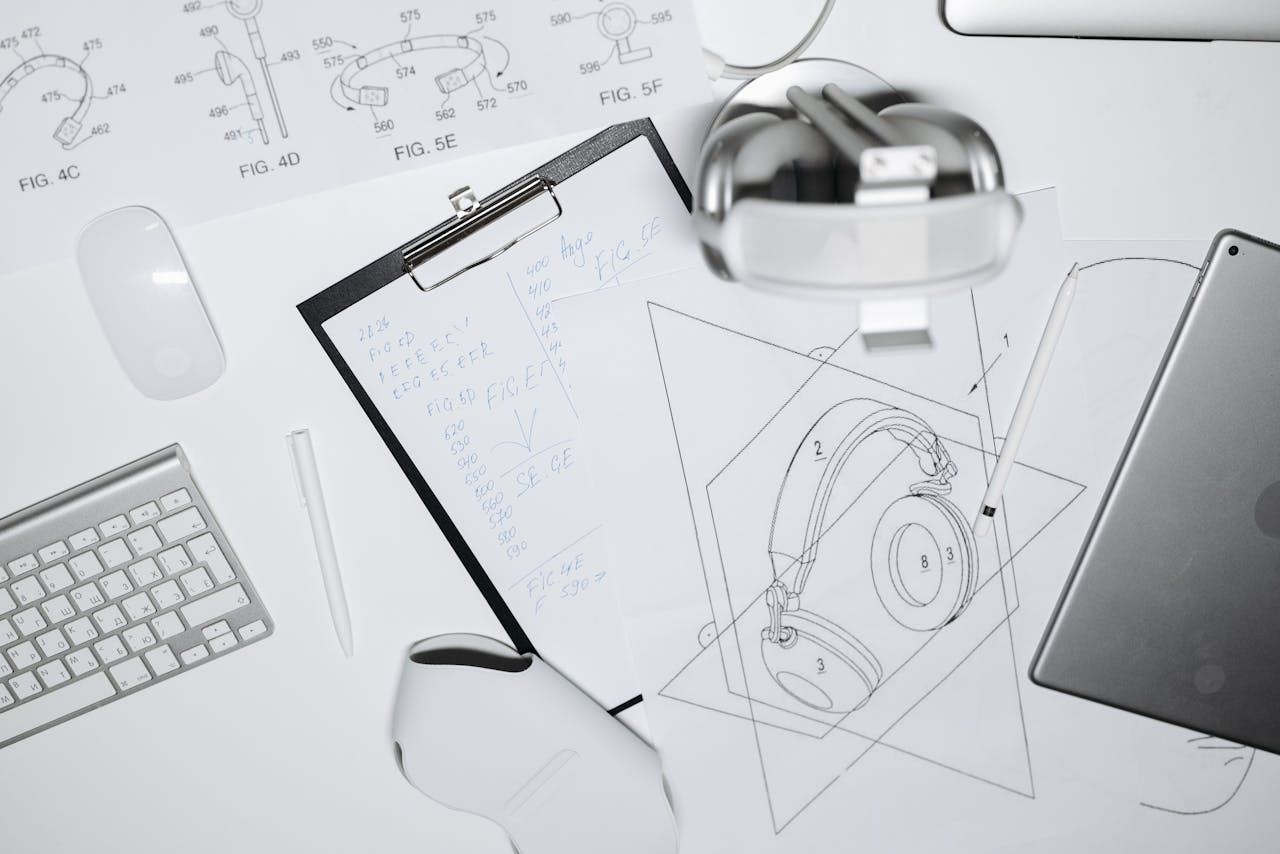
Utility patents cover the functional aspects of an invention, such as how it works, its structure, and its method of operation. Drawings serve to illustrate these features clearly and comprehensively. The United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) has specific requirements for these drawings, which must be adhered to in order to meet patent submission standards.
Key Elements of Utility Patent Drawings
- Clarity and Detail
- The primary goal of patent drawings is to provide a clear representation of the invention. Drawings should be detailed enough to convey essential features and functionality but not so cluttered that they confuse the viewer. Each component should be labeled accurately to avoid ambiguity.
- Standardization
- Patent illustrations must conform to specific formatting standards set forth by the USPTO. These include size, margins, and line thickness. Typically, drawings are created at a readability scale of 1:1 or 1:1.5, ensuring that the text and figures remain legible and consistent throughout the document.
- Use of Multiple Views
- Often, a single view of an invention may not capture all its functional elements. Including multiple views—such as top, front, side, and cross-sectional perspectives—can provide a complete understanding of the invention’s structure and operation. Such representations can showcase how parts interact, enhancing the patent examiner’s comprehension.
- Descriptive Legends
- Each drawing should be accompanied by descriptive legends where necessary. These legends explain the purpose and function of the various components, aiding in clarity. Proper labeling ensures that the reader can easily identify the elements in the drawing that are critical to understanding the invention.
- Quality of Execution
- The execution of patent drawings must be of the highest quality. Whether hand-drawn or digitally produced, the lines must be clean, and the overall presentation must be professional. Poor-quality illustrations can lead to misunderstandings and potentially jeopardize the patenting process.
- Avoiding Ambiguities
- Ambiguities in patent drawings can raise questions during examination and may lead to the rejection of a patent application. It’s crucial to ensure that every line and label is thoughtfully placed to represent the invention accurately. The drawings must leave little to no room for misinterpretation.